Ubuntuでは、rootは使わずsudoコマンドを使うのが一般的です。
- その設定ファイルは、/etc/sudoersにあります。
- ファイルのパーミションは、rootでReadOnlyです。
- 編集する場合には、sudoeditを使用します。
sudo sudoedit /etc/sudoers#
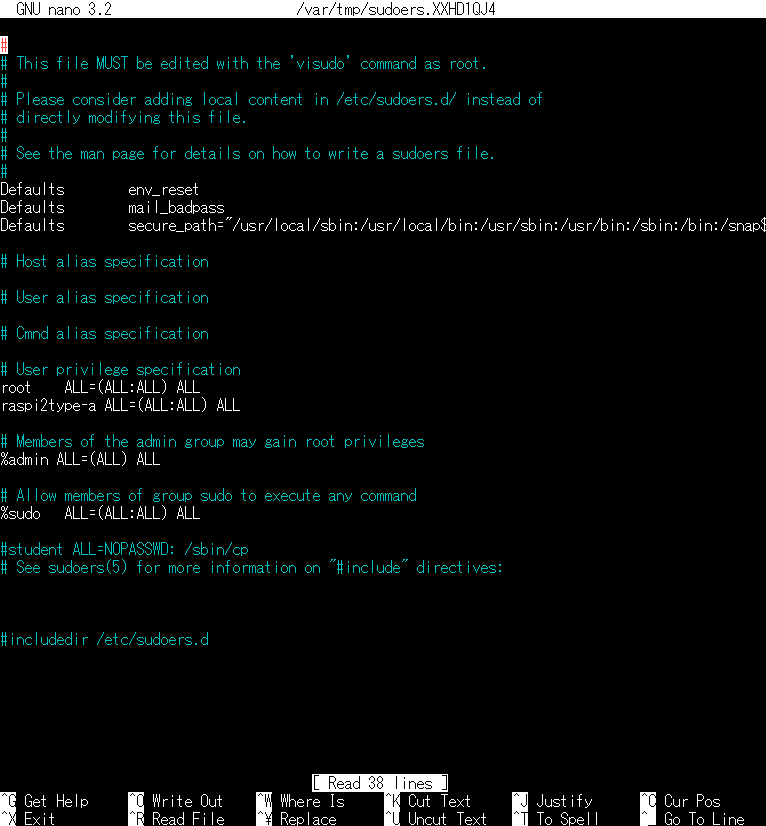
# This file MUST be edited with the 'visudo' command as root.
#
# Please consider adding local content in /etc/sudoers.d/ instead of
# directly modifying this file.
#
# See the man page for details on how to write a sudoers file.
#
Defaults env_reset
Defaults mail_badpass
Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap$
# Host alias specification
# User alias specification
# Cmnd alias specification
# User privilege specification
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
# Members of the admin group may gain root privileges
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
# Allow members of group sudo to execute any command
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
#student ALL=NOPASSWD: /sbin/cp
# See sudoers(5) for more information on "#include" directives:
#includedir /etc/sudoers.d- Ctrl + x ⇒ Y と打ち込むとFile name to write : /var/tmp/sudoers.XXXXXX と出力されるのでリターンキーの押下し、保存します。
- sudo を全て許容するユーザーは、userNamet ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL の行を追加します。
cpコマンドだけ、パスワードなしで実行できるユーザーをstudentとすると、以下のようになります。
student ALL=NOPASSWD: /sbin/cpUbuntuの初期ユーザーは、sudoグループに属しているため /etc/sudoers のファイル内には現れません。
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL例えばstudentが初期ユーザーの場合、/etc/groupは以下のようにsudoグループに登録されています。グループ名:シャドウパスワード:グループID:ユーザーリスト(カンマ区切り)
sudo:x:27:student